The kitchen is now the heart of the house, a space where we cook, eat, meet, work and where our children play or do their homework. This diversity of functions implies a proliferation of germs, and it is necessary to take extreme precautions to avoid the creation of contamination sources in this room.
According to several investigations, more than half of the domestic food toxiinfections are due to incorrect hygiene habits in the kitchen. One of the measures to avoid the presence of microorganisms that cause this type of health problems is to identify the areas most prone to contamination and keep them clean and dry.
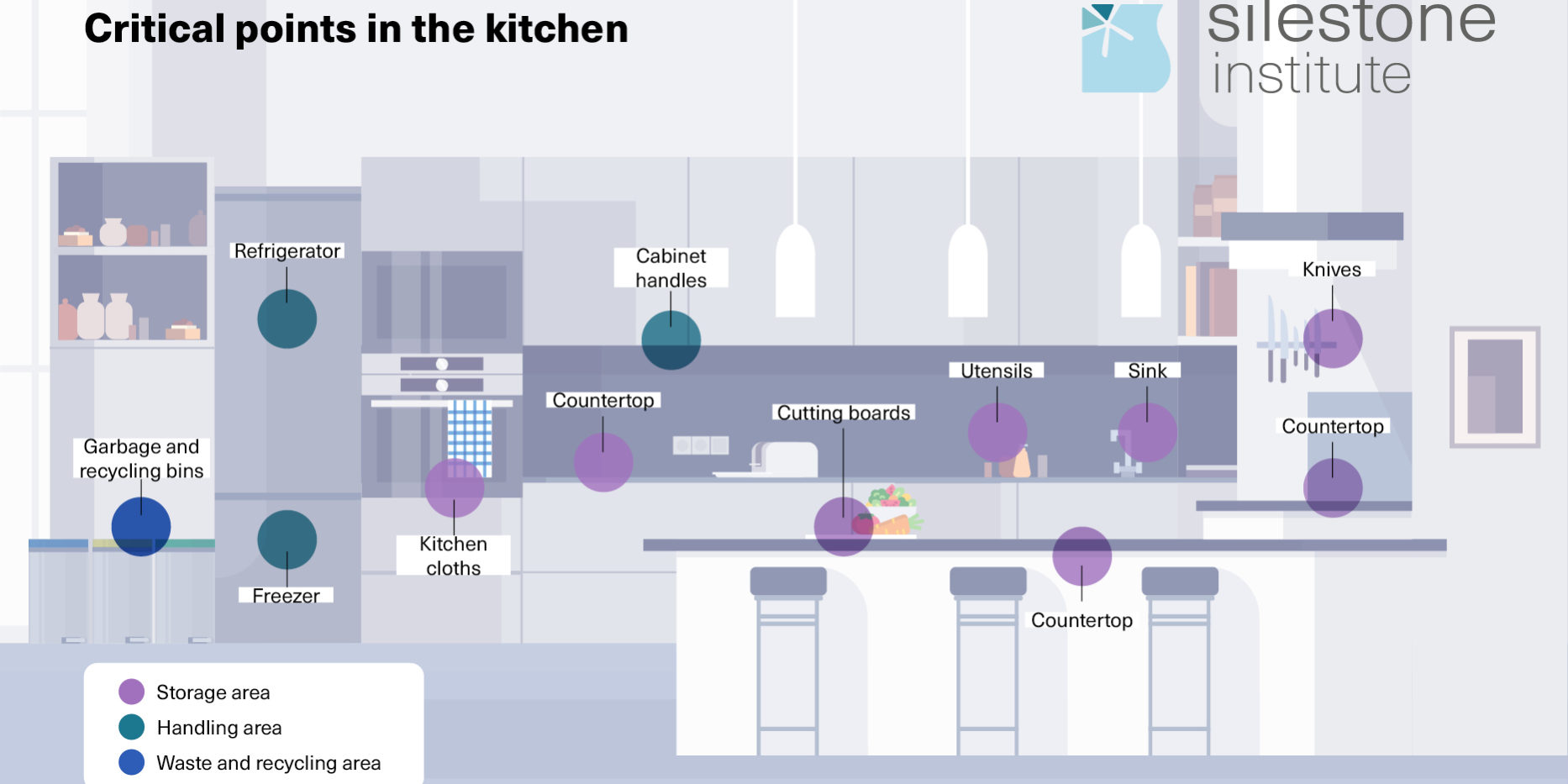
The Silestone Institute explains which are the critical points in the kitchen where germs can proliferate and offers practical advice to prevent the toxiinfections they can cause.
STORAGE AREA
The pantry
It should be a cool, dry and ventilated place. It should be cleaned regularly and the condition and expiration date of stored foods should be checked.
Refrigerator and freezer
For the correct preservation of food, the indicated temperatures are between 1º C and 4º C in the refrigerator and below -18º C in the freezer. It is important the periodic cleaning of these appliances to avoid frost, making it easier to maintain the indicated temperatures. We must not forget to clean the handles, since a large number of bacteria are concentrated in them, nor avoid overloading the refrigerator, since this will prevent the cold air from circulating freely and being distributed homogeneously. Place prepared foods preferably on the upper shelves in airtight containers to avoid cross-contamination between products.
HANDLING AREA
It is essential that all equipment and work materials that come into contact with food be made of materials that are easy to clean and disinfect, as well as being corrosion resistant.
Sink
The sink is the wet spot in the kitchen, so be extra cautious. Remove all food debris, sanitize and dry it after use.
Countertop
Surfaces where food is prepared are areas where cross-contamination can easily occur, as food debris and moisture can create an ideal environment for the reproduction of bacteria that are harmful to health. Remove food debris, clean and dry the surface well with the appropriate product recommended by the manufacturer for cleaning and preservation.
Utensils
You must not forget to clean utensils every time you change the food handled, to eliminate possible germs that may have been left by the previous food.
Cutting boards
Cutting boards are materials prone to contamination and have a high level of risk. For this reason, the board should be cleaned and dried every time the food is changed.
Knives
It is important to clean the knife every time we change from a handled food or from a raw food to a ready-to-eat food. If, for example, we cut a contaminated raw chicken breast that is going to be cooked even if the bacteria are later eliminated by the heat, and with the same knife we cut the tomato for the salad, it will end up being contaminated.
Kitchen cloths and rags
They are one of the materials most prone to contamination. Therefore, they should be changed daily or whenever they get dirty due to their high risk level. Another option is to use disposable paper rolls.
WASTE AND RECYCLING AREA
Waste is an important source of contamination due to its richness in organic matter. This area is therefore a high-risk zone in which we must be very meticulous with its cleanliness.
Garbage and recycling bins
The garbage bin should always be covered and once emptied – something that must be done daily and whenever it is full – it should be cleaned and disinfected properly with a suitable product. It is also important to clean and disinfect the various recycling containers where germs can also proliferate.
In addition, we cannot forget the cleaning of floors, ceilings, hoods, switches, cabinet handles, etc., since they can accumulate remains of food and humidity. It is not a question of sterilizing the environment in which we live, but of reducing the amount of pathogenic agents that cause diseases that exist in it, so that they are not harmful to our health or to the health of those around us.